In enterprise environments, it’s often necessary for users in one Active Directory (AD) forest to access resources in another. This is where trust relationships come into play. These trusts are commonly used during mergers, acquisitions, or cross-organization integrations.
This guide walks you through setting up a two-way trust relationship between two separate forests—contoso.loc and test.loc.
What Is a Trust Relationship?
A trust allows authentication across AD domains. With it, users from one forest can securely access resources in another. However, these trusts must be configured between the root domains of each forest.
Prerequisites
Before configuring a trust, ensure the domain controllers from both forests can communicate with each other and resolve DNS names correctly. This is achieved by configuring DNS Conditional Forwarders.
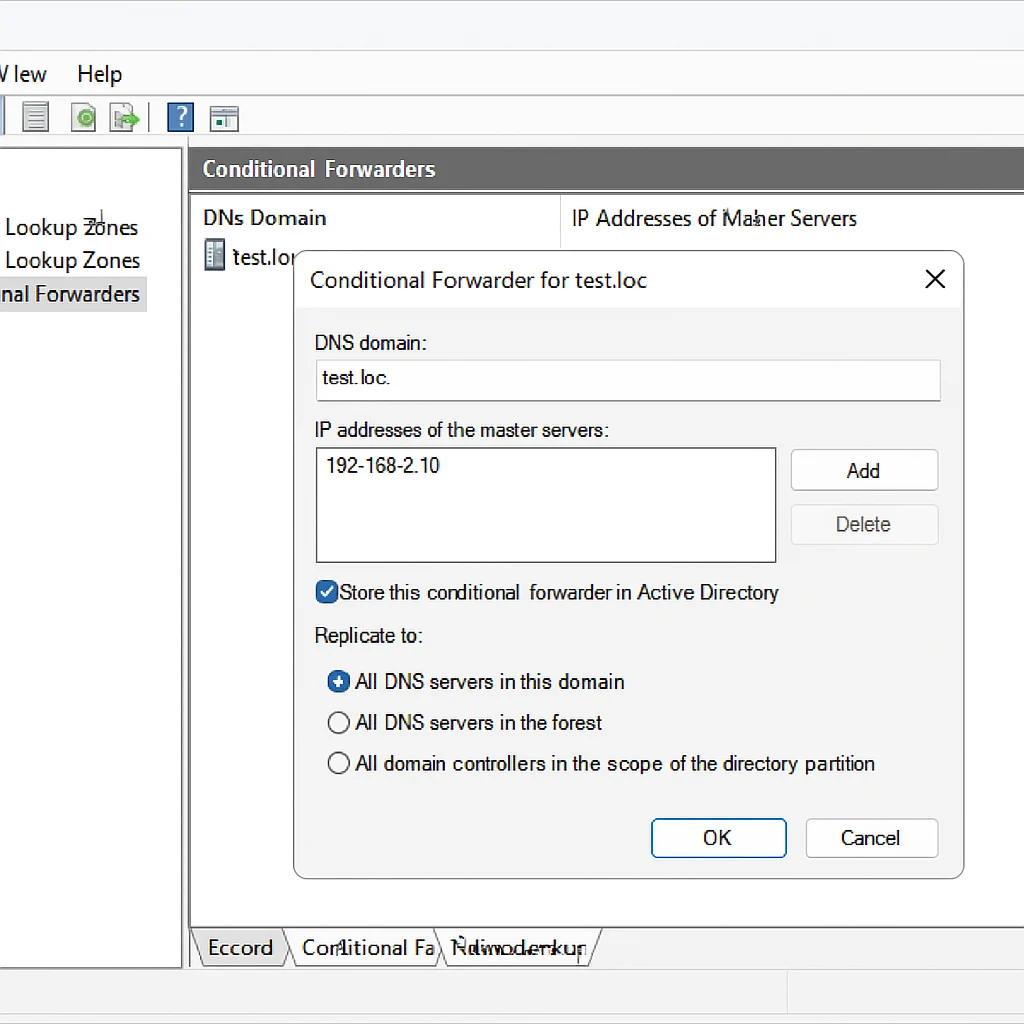
Set Up Conditional Forwarding:
- Open DNS Manager (
dnsmgmt.msc) on thecontoso.locdomain controller. - Navigate to Conditional Forwarders.
- Create a new forwarder for
test.loc:- Enter the domain name (
test.loc) - Add the IP address of the domain controller from
test.loc - Enable “Store this conditional forwarder in Active Directory”
- Replicate to All DNS servers in this domain
- Enter the domain name (
- Repeat the same on the
test.locdomain controller forcontoso.loc.
Configure the Trust Relationship
After DNS is correctly set up, follow these steps:
- Launch Active Directory Domains and Trusts (
domain.msc) oncontoso.loc. - Right-click your domain, go to Properties, and open the Trusts tab.
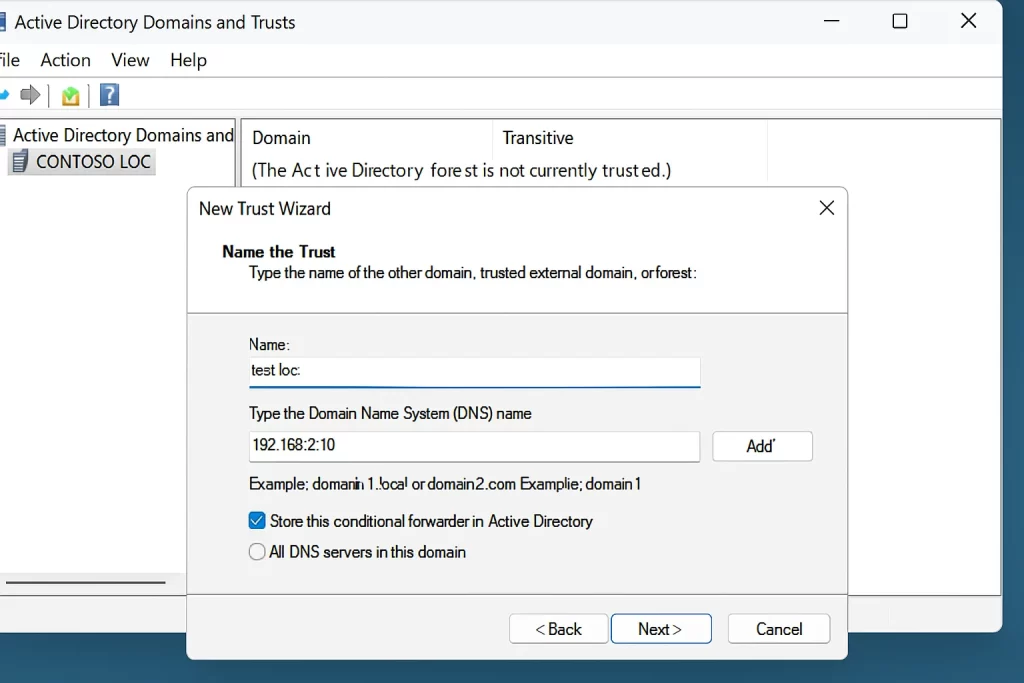
- Click New Trust and launch the wizard.
- Enter the name of the other domain (
test.loc). - Choose the trust type:
- External Trust: A one-to-one trust between root domains (non-transitive).
- Forest Trust: Transitive trust across all child domains within each forest.
- Choose the trust direction:
- Two-way: Both domains trust each other.
- One-way incoming: Only your domain accepts users from the other.
- One-way outgoing: Your users can access the other domain’s resources.
- Decide where to create the trust:
- This domain only
- Both this domain and the specified domain
- Enter credentials of a user in
test.locwith Enterprise Admin rights. - Choose authentication scope for users from
test.loc:- Domain-wide authentication: Full access within your domain.
- Selective authentication: Only specific resources can be accessed.
- Configure outbound authentication rules for your own users.
- Proceed through the wizard and verify that the trust was successfully established.
SID Filtering Warning
Once the trust is active, you may see a security warning about SID filtering. By default, AD filters out Security Identifiers (SIDs) from trusted domains to protect against token spoofing.
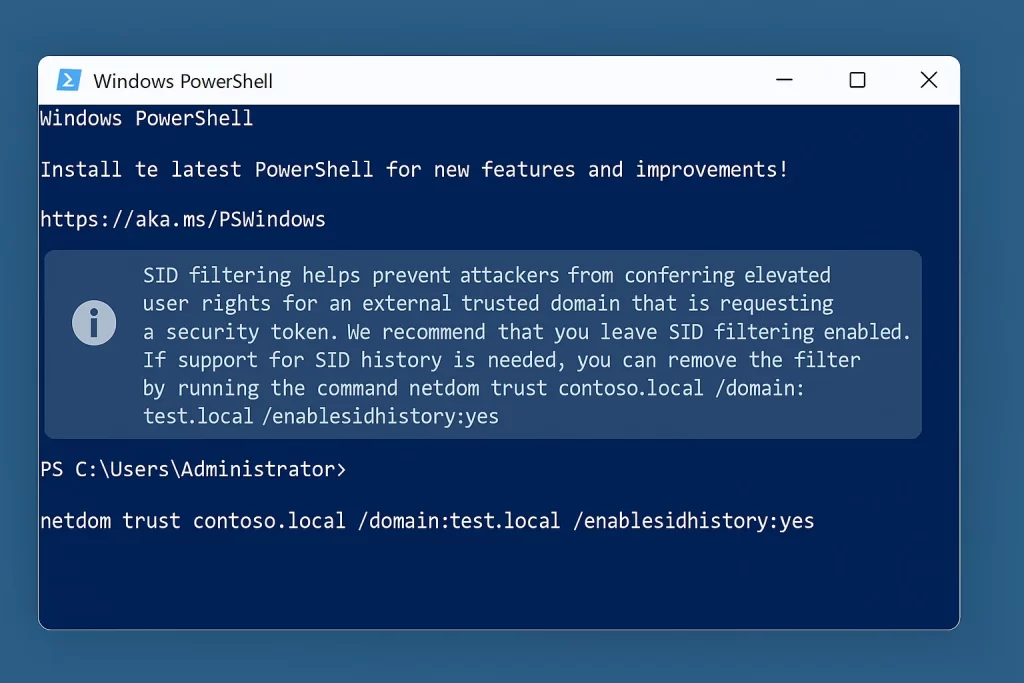
If you are migrating users and need SID History, you can temporarily disable filtering using this command:
netdom trust contoso.loc /domain:test.loc /quarantine:No🔒 Be cautious—only disable SID filtering during controlled migrations.
Conclusion
Establishing trust relationships between AD forests is essential for enabling cross-domain authentication and collaboration. By configuring DNS properly and using the Trust Wizard, you can securely connect environments and streamline resource sharing.
Morris James
I am a Infrastructure & DevSecOps Engineer with over a decade of experience in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and automation. As the founder of Infotech Ninja, I share my expert insights on IT strategy, system administration, and security best practices. Holding certifications like CCNP Enterprise, MCSE, and VCP-DCV, I specialize in optimizing IT infrastructures and leveraging automation to drive efficiency.
